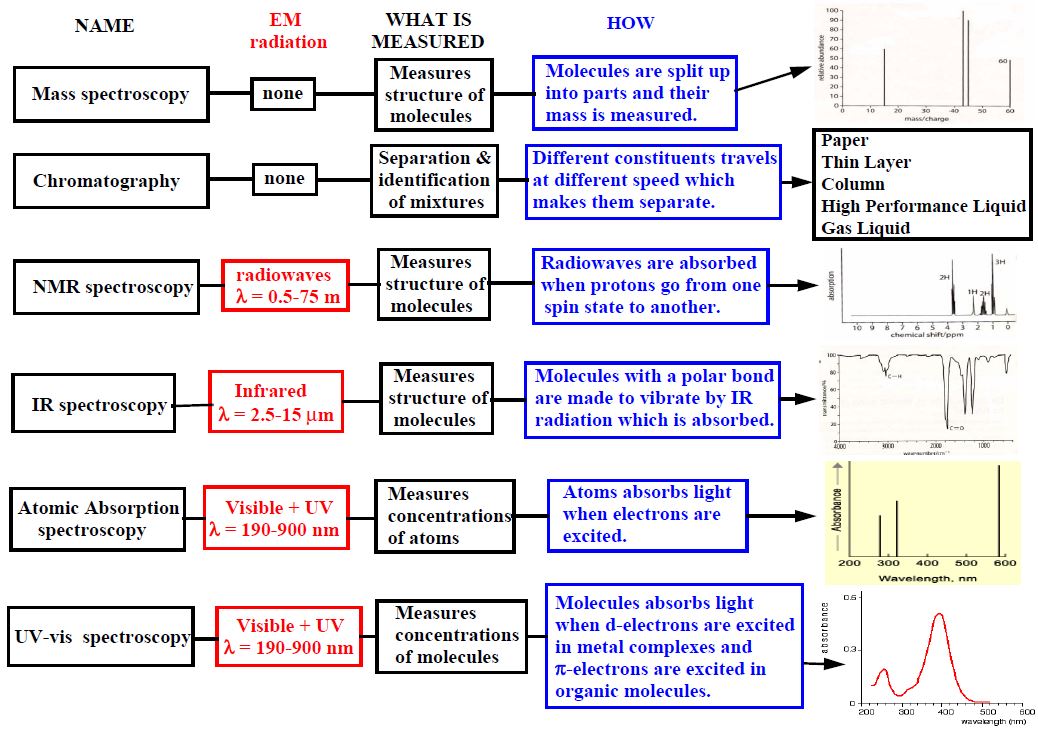
1 - What are the different types of analysis ?
2 - What methods can be used to give information about the molecule structure ?
3 - Summarize all the methods !
3 - Describe what electromagnetic radiation is.
4 - What is the formula for the energy and wavelength of a photon ?
6 - Describe the electromagnetic spectrum.
7 - What is an absorption and emission spectrum ?
8 - How can infrared radiation be used to excite a molecule ?
9 - What sort of movement in the molecule can the IR radiation induce ?
10 - How does the wavenumber depend on the bond type in diatomic molecules ?
11 - How does the wavenumber depend on the vibrational mode in polyatomic molecules ?
12 - Only two vibrational modes are active for the carbon dioxide molecule. Why ?
13 - What are the characteristic wavenumber for different bonds ?
14 - Explain how a double-beam IR spectrometer works !
15 - Analyse 
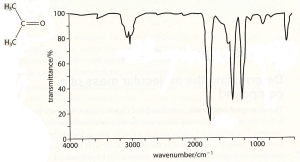
16 - Analyse 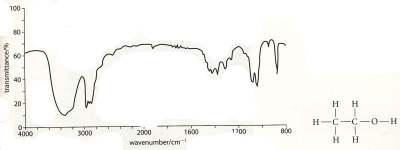
17 - Describe how a mass spectrometer works.
18 - Describe how a mass spectrometer can be used to get information about the molecular spectrum.
19 - Solve 
20 - Describe how a NMR spectrometer works.
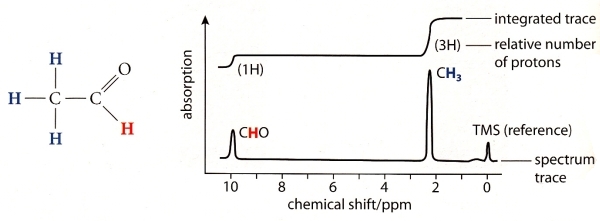
21 - What is the chemical shift ?
22 - What are the characteristic chemical shifts for hydrogen atoms in different chemical environments ?
23 - What is shown here: 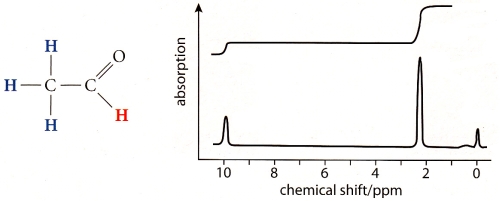
24 - NMR spectrum of C3H8O: 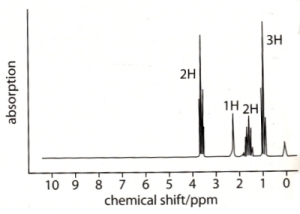
Which formula is correct: 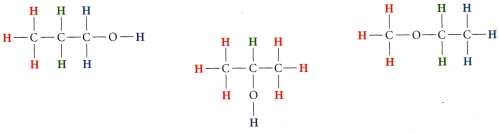
25 - What is MRI ?
26 - Why is TMS used as a reference sample ?
27 - What would this look like in high-resolution NMR:

28 - What is causing the splitting of the peaks ?
29 - Explain the details of the NMR spectrum above.
30 - What is the different height of the peaks caused by ?
31 - How does AA spectroscopy work ?
32 - What is a calibration curve and how it is used ?
33 - What is a ligand ?
34 - How does ligands affect the energy levels of transition metals ?
35 - Why does transition metals with ligands such as [Cu(H2O)6]2+ appear coloured ?
36 - How does UV spectroscopy work ?
37 - What factors affect the colour of transition metal complexes ?
38 - What is a conjugated system ?
40 - Why are carrots not blue ?
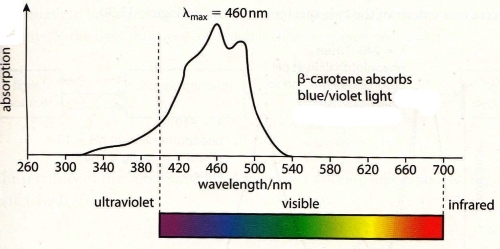
41 - Why does the colour in acid-base indicators change ?
44 - What is absorption and adsorption ?
45 - Explain the difference between adsorption chromatography and partition chromatography !
46 - Give examples of adsorption chromatography and partition chromatography !
47 - Explain how paper chromatography works !
48 - What is the retention factor ?
49 - Explain how Thin-Layer Chromatography (TLC) works !
50 - What are the advantages of TLC compared to paper chromatography ?
51 - Explain how column chromatography works !
52 - What are the advantages of column chromatography ?
53 - Explain how gas-liquid chromatography (GLC) works !
54 - Explain how the detector in GLC works !
55 - What is the difference in the chromatogram in GLC compared to that of TLC and paper chromatography ?
56 - When is gas-liquid chromatography used ?
57 - What alcohols are causing these GLC peaks:
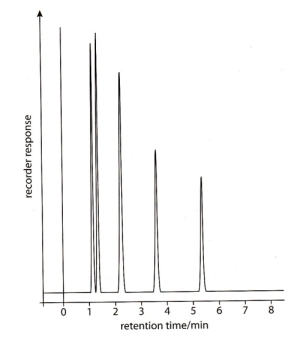
58 - Explain how High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) works !
59 -
What are the advantages of HPLC ?
Go back to the IB chemistry page
Go to the IB physics page
The wavenumber is the inverse of the wavelength. Its unit is cm-1
Wavenumber = 1 / λ
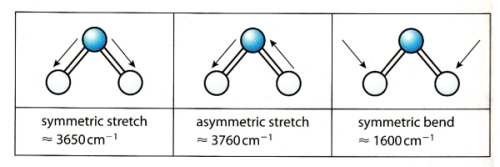
Wavenumber of asymmetric stretch > Wavenumber of symmetric stretch > Wavenumber of symmetric bend
Compare a low-resolution NMR spectrum with a high-resolution one:

Column chromatography is used when large amounts of a sample have to be separated.
GLC is used for samples that can be vaporized without decomposition.