Bonding IB1
1. What is the formula for the compound formed by calcium and nitrogen?
A. CaN
B. Ca2N
C. Ca2N3
D. Ca3N2
ANSWER
(Total 1 mark)
2. Explain why the bonds in silicon tetrachloride, SiCl4, are polar, but the molecule is not.
(Total 2 marks)
3. Element X is in group 2, and element Y in group 7, of the periodic table. Which ions will be present in the compound formed when X and Y react together?
A. X+ and Y–
B. X 2+ and Y–
C. X+ and Y2–
D. X2– and Y+
ANSWER
(Total 1 mark)
4. Which statement is correct about two elements whose atoms form a covalent bond with each other?
A. The elements are metals.
B. The elements are non-metals.
C. The elements have very low electronegativity values.
D. The elements have very different electronegativity values.
ANSWER
(Total 1 mark)
5. Which statement is true for most ionic compounds?
A. They contain elements of similar electronegativity.
B. They conduct electricity in the solid state.
C. They are coloured.
D. They have high melting and boiling points.
ANSWER
(Total 1 mark)
6. Which fluoride is the most ionic?
A. NaF
B. CsF
C. MgF2
D. BaF2
ANSWER
(Total 1 mark)
7. Which statement is a correct description of electron loss in this reaction?
2Al + 3S → Al2S3
A. Each aluminium atom loses two electrons.
B. Each aluminium atom loses three electrons.
C. Each sulfur atom loses two electrons.
D. Each sulfur atom loses three electrons.
ANSWER
(Total 1 mark)
8. Which compound contains both ionic and covalent bonds?
A. MgCl2
B. HCl
C. H2CO
D. NH4Cl
ANSWER
(Total 1 mark)
9. Which statement is true for compounds containing only covalent bonds?
A. They are held together by electrostatic forces of attraction between oppositely charged ions.
B. They are made up of metal elements only.
C. They are made up of a metal from the far left of the periodic table and a non-metal from the far right of the periodic table.
D. They are made up of non-metal elements only.
ANSWER
(Total 1 mark)
10. The diagrams below represent the structures of iodine, sodium and sodium iodide.
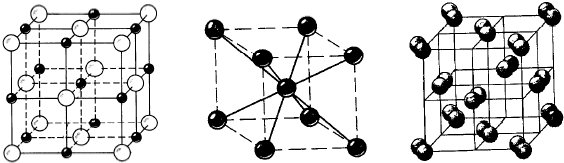
A B C
(a) (i) Identify which of the structures (A, B and C) correspond to iodine, sodium and sodium iodide.
(1)
(ii) State the type of bonding in each structure.
(3)
(b) (i) Sodium and sodium iodide can both conduct electricity when molten, but only sodium can conduct electricity when solid. Explain this difference in conductivity in terms of the structures of sodium and sodium iodide.
(4)
(ii) Explain the high volatility of iodine compared to sodium and sodium iodide.
(2)
(Total 10 marks)
11. (i) State the full electron configuration for argon.
(1)
(ii) Give the formulas of two oppositely charged ions which have the same electron configuration as argon.
(2)
(Total 3 marks)
12. (a) Use the Aufbau principle to write the electron configuration of an atom of germanium.
(1)
(b) The successive ionization energies of germanium are shown in the following table:
|
1st |
2nd |
3rd |
4th |
5th |
|
Ionization energy / |
760 |
1540 |
3300 |
4390 |
8950 |
(i) Identify the sub-level from which the electron is removed when the first ionization energy of germanium is measured.
(1)
(ii) Write an equation, including state symbols, for the process occurring when measuring the second ionization energy of germanium.
(1)
(iii) Explain why the difference between the 4th and 5th ionization energies is much greater than the difference between any two other successive values.
(2)
(Total 5 marks)
13. (i) Explain why successive ionization energies of an element increase.
(1)
(ii) Explain how successive ionization energies account for the existence of three main energy levels in the sodium atom.
(3)
(Total 4 marks)