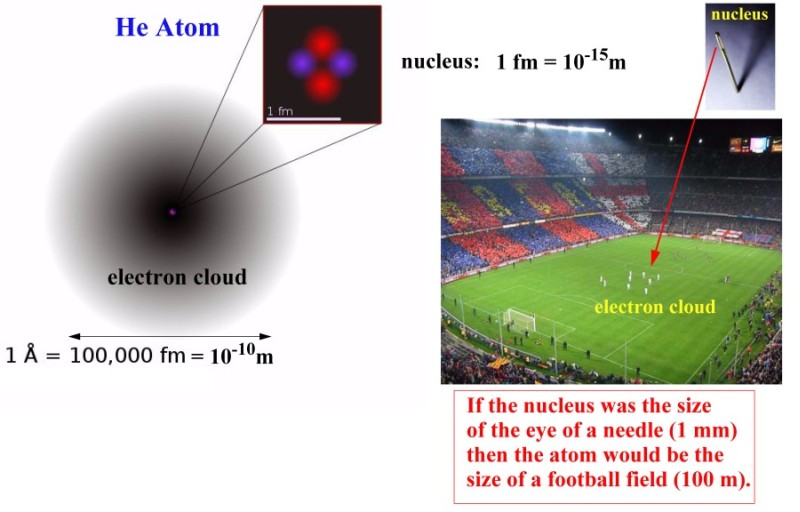
1 - What is the size of an atom ?
2 - Describe Rutherford's experiment.
4 - Describe one problem with the Bohr model.
5 - What is atomic energy levels ?
6 - Describe an experiment with hydrogen that shows that atomic energy levels exists ?
7 - What is Z ?
8 - What is N ?
9 - What is A ?
10 - Write down the atomic symbol for an Aluminium atom that has 14 neutrons and 13 electrons.
11 - What is a nuclide ?
12 - What is an isotope ?
13 - What is a nucleon ?
14 - What is an ion ?
15 - What is a unified atomic mass unit ?
16 - What is the mass of a neutron, proton and electron in unified atomic mass units and kg ?
17 - What is the elementary charge unit ?
18 - What is the charge of a neutron, proton and electron in elementary charge units and Coulomb ?
20 - What is the nuclear force (also called "the strong force") ?
21 - What is an eV and a MeV ?
22 - What is the binding energy ?
23 - What is Einstein's famous formula and what does it mean ?
24 - What is the mass defect ?
25 - How can you convert the mass in kg to mass in u or mass in MeV ?
26 - The mass of a He-3 nucleus is 3.0160 u. What is the binding energy per nucleon in MeV ?
27 - Draw a binding energy curve and explain what it tell us ?
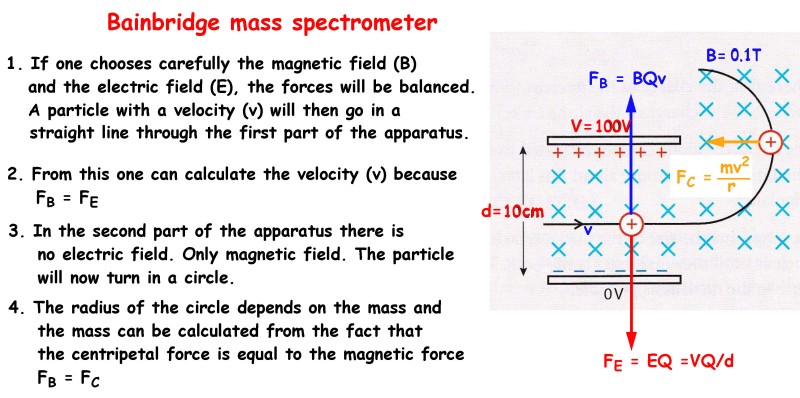
28 - Explain how a Bainbridge mass spectrometer work and draw a picture.
29 - What is natural radioactive decay ? And why are some nuclei stable and others not ?
30 - What is alpha decay and alpha radiation ?
32 - What is beta decay and beta radiation ?
33 - What is gamma decay and gamma radiation ?
34 - What does alpha, beta and gamma energy distributions looks like ?
35 -
In the reaction B → C + β + ν the total binding energy of B is 79 MeV and the total binding
energy of C is 92 MeV.
What is the energy of the beta particle ?
36 - What is the reaction when 1327Al decays with alpha, beta and gamma radiation ?
37 - What is ionising radiation ?
38 - What is a Geiger-Muller detector ?
39 - What is the properties of different types of radiation ?
40 - What does it mean that radioactive decays are a random process ?
41 - What does radioactive half-life mean ?
42 - What does a decay curve looks like for different decay constants ?
43 - What does the decay equation that give the decay curve look like ?
44 - What is the relationship between the decay constant and the half-life ?
45 - How can you determine the half-life from a decay curve ?
46 - What does the activity equation look like ?
47 - What is the difference between A and N ?
48 - How does Potassium-argon dating work ?
49 -
You have 1011 K-40 nuclei.
After 1011 years only 58% is left.
What is the decay constant of K-40 ?
50 -
You have 1011 K-40 nuclei.
55 nuclei decay in one year.
What is the decay constant of K-40 ?
51 - How does Carbon dating work ?
53 - Give an example of a transmutation ?
54 - What is the process called that gives energy to the sun ?
55 - What is the process called that gives energy in a nuclear power plant ?
57 - Explain what fission is ?
Z = the number of protons in the nucleus.
N = the number of neutrons in the nucleus.
A = Z + N = the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus.
A unified atomic mass unit (u) is defined as the mass of 1/12 of the nucleus of a carbon-12 isotope.
An elementary charge unit (e) is defined as the (opposite sign) charge of one electron.
7.6 - Radioactive decay
1327Al → 24He + 1123Na
1327Al → e- + ν + 1427Si
1327Al → γ + 1327Al
7.7 - Half-life
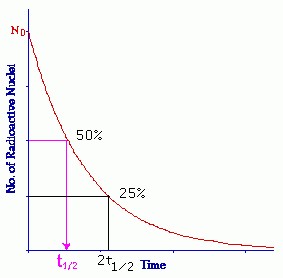
The half-life is the time it takes for half of a sample of unstable nuclei to decay.
Look at the data booklet: 
T1/2: Half-life in s.
λ: the decay constant in s-1.
ln(2) = 0.693....
Look at which time 50% of the original sample is left:
7.8 - nuclear reactions