1 - Describe what the Lewis theory is.
3 - How are pH, pOH and pKw defined ?
4 - What is the relationship between pH, pOH and pKw ?
5 - What happens with [H+] and [OH-] if one doubles the concentration of an acid ?
6 - How are Ka and Kb defined ?
7 - What does the value of Ka tell you ?
9 - What is the relationship between Ka and Kb ?
10 - What are the values of Ka, pKa, Kb and pKb for strong acids and bases.
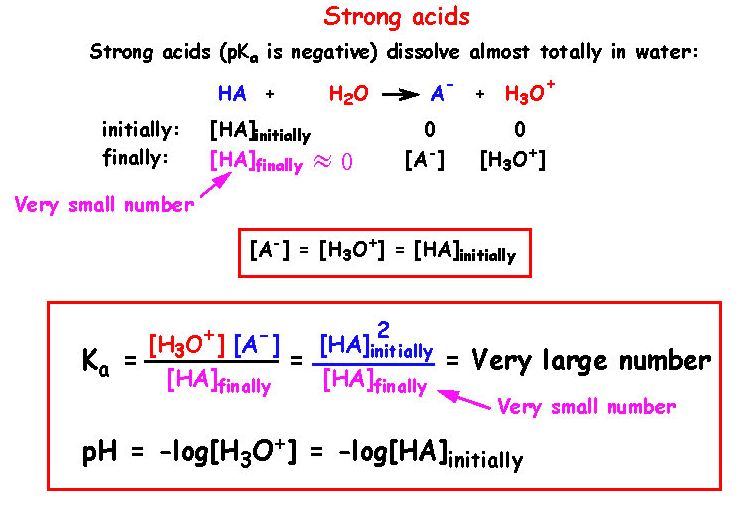
11 - How can the calculation of Ka be simplified for a strong acid ?
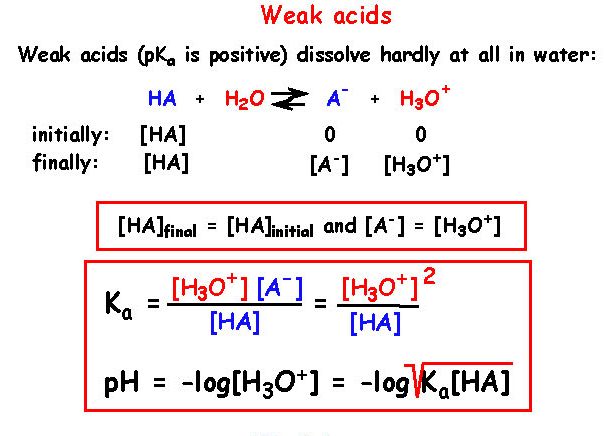
12 - How can the calculation of Ka be simplified for a weak acid ?
13 - What is the purpose of a buffer solution ?
14 - What does a buffer solution consist of ?
15 - What is the basic principle of a buffer solution ?
16 - What is the detailed principle of a buffer solution ?
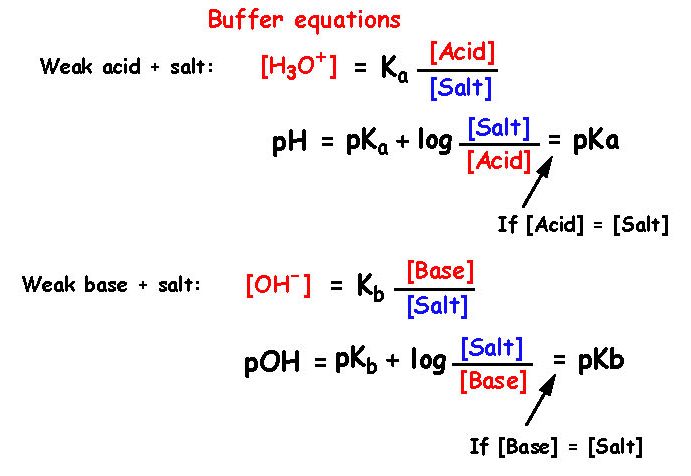
17 - What are the equations that describe a buffer solution ?
18 - What factors influence a buffer ?
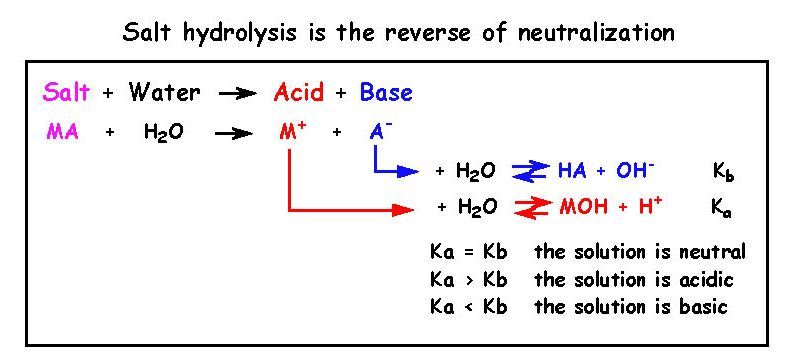
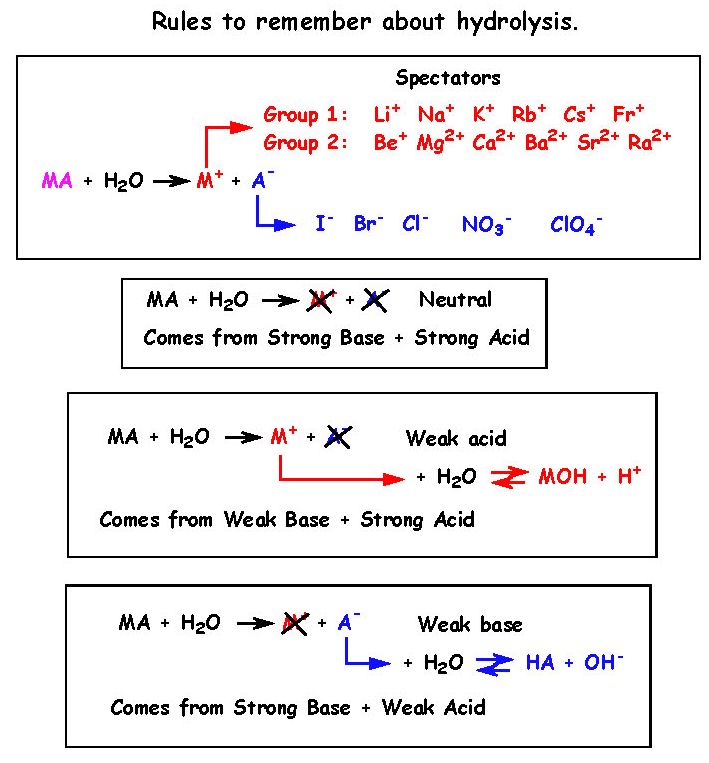
19 - What is salt hydrolysis and what is the reaction for it ?
20 - What is a spectator ion and which ions are spectators ?
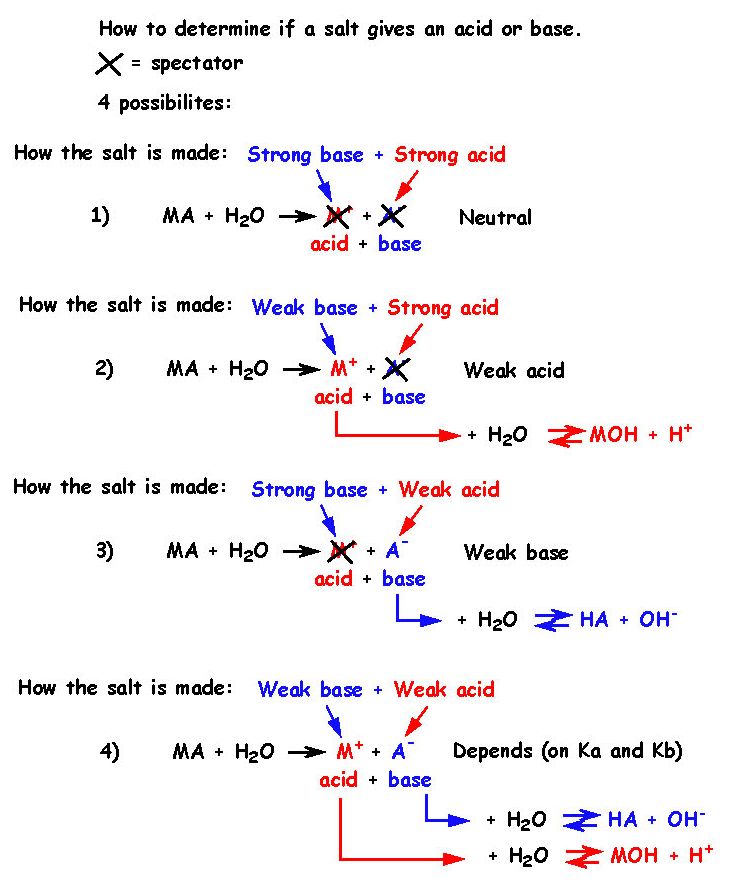
21 - How can one determine if a salt gives and acid or a base ?
22 - What are the rules to remember ?
23 - Draw and explain the titration curve for a strong acid with a strong base ?
24 - Draw and explain the titration curve for a weak acid with a strong base ?
25 - Draw and explain the titration curve for a strong acid with a weak base ?
26 - Draw and explain the titration curve for a weak acid with a weak base ?
27 - Draw and explain the titration curve for a base with an acid ?
28 - What is half-equivalent point and how can it be used ?
30 - How does an indicator work ?
31 - What is the endpoint of an indicator ?
32 - How is indicators used during titrations ?
34 -
What are the pH ranges of equivalence for different acid-base combinations
and suitable indicators ?
Download notes on acids.
Go back to the IB chemistry page
Go to the IB physics page
A Lewis acid is defined as a species which accepts an electron pair to form a covalent bond.
A Lewis base is a species which donates an electron pair to form such a bond. This is a special
type of covalent bond because the bond is formed by two electrons from one species and none from
the other. This often occurs in the formation of complex ions. In Bronsted-Lowry acid/base reactions
a H+ accepts a pair of electrons since it has not electrons of its own to form a bond.
Note, however, that Lewis theory is more general than Bronsted-Lowry theory.
In pure water there is the following very rare reaction:
H2O(l) <=> H+(aq) + OH-(aq).
Kw=[H+][OH-]
The value of Kw is 1 x 10-14 at 25 Co, but varies with temperature.
pH = -log[H+] (pH is the negative log of the concentration of H+ ions)
pOH = -log[OH-]
pKw = -log([H+][OH-]) = 14 at 25 Co
pH + pOH = pKw = 14 at 25 Co
[H+] and [OH-] are directly related to the concentration of the acid/base. Doubling the concentration of the acid will double [H+] and halve [OH-], and the vice versa for bases.
The reaction for a general acid can be written as:
HA(aq) <=> H+(aq) + A-(aq)
Ka is then defined as
Ka = [H+][A-]/[HA]
The reaction for a general base can be written as:
B(aq) + H2O(l) <=> BH+ + OH-(aq)
Ka is then defined as
Kb = [BH+][OH-] / [B]
Ka is a constant which describes the ionisation of an acid (i.e. how strong it is) and Kb does the same for bases.
pKa = -log(Ka)
pKb = -log(Kb)
As with the pH scale, a 1 fold change in pKa or pKb will signify a tenfold change in Ka or Kb.
Ka x Kb = Kw = 1 x 10-14 at 25 Co
pKa + pKb = pKw = 14 at 25 Co
Strong acids have weak conjugate bases and strong bases have weak conjugate acids. A strong acid has a large Ka value (or a small pKa value) and a strong base, likewise, has a large Kb value and a small pKb value. Strong acids typically have negative pKa values. Strong bases typically have a pKb value around zero.

A buffer solution is resistant to changes of its pH when small amounts of acid or base is added to it. Note that it has to be small amounts.
A buffer solution is composed of a weak acid and it's conjugate base or a weak base and it's conjugate acid.
The acid in the buffer will neutralize an added alkali and the base in the buffer will neutralize
any added acid.

Dilution If one put more water into a buffer it will not change pH but its ability
to absorb acids and alkalis becomes smaller
Temperature If temperature changes then Ka and Kb changes and with that the pH. It is therefore
important to use a buffer at a constant temperature.


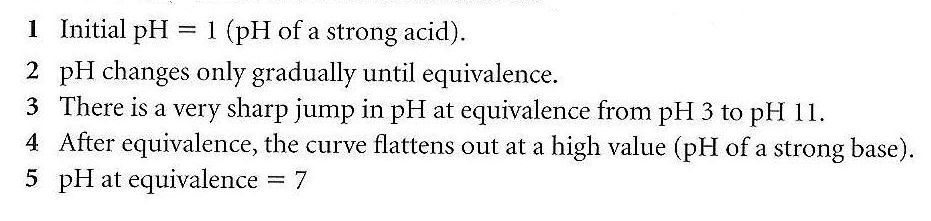
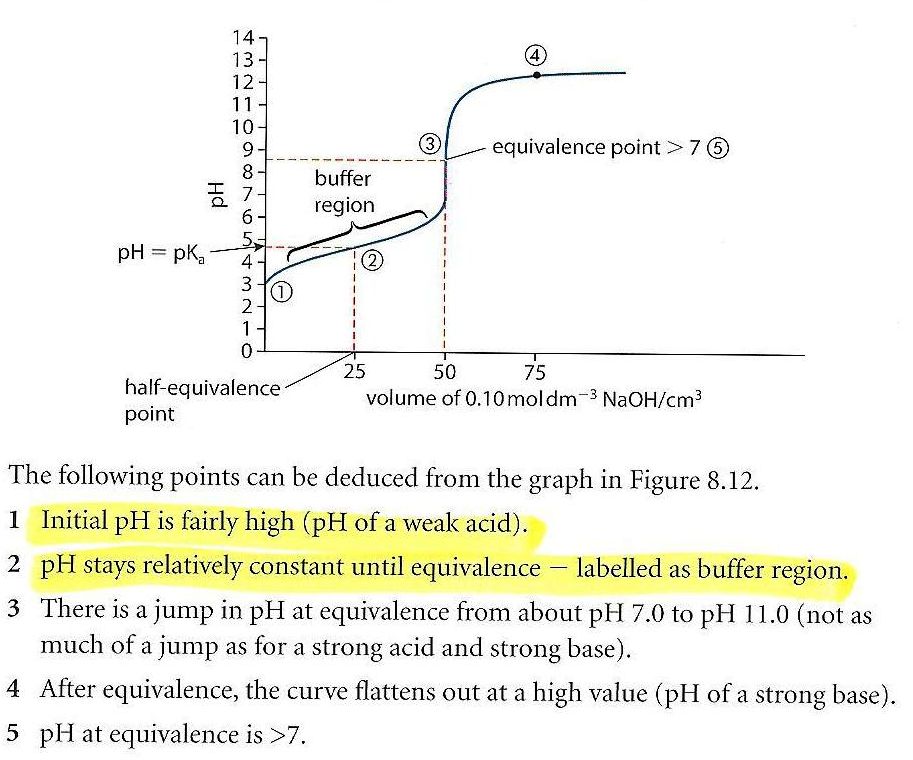
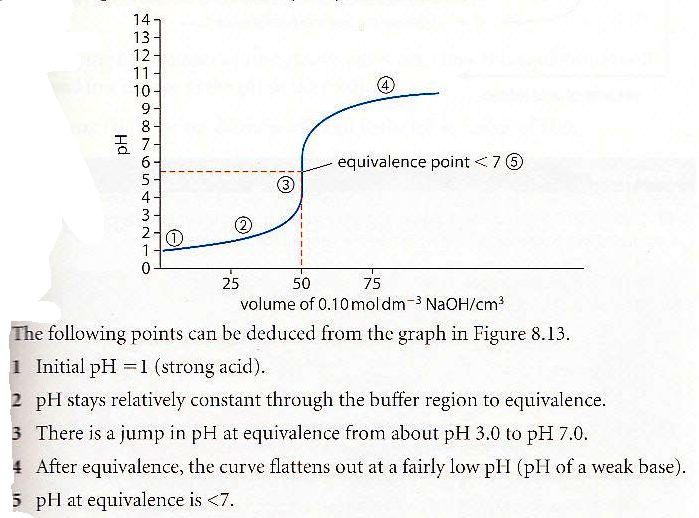
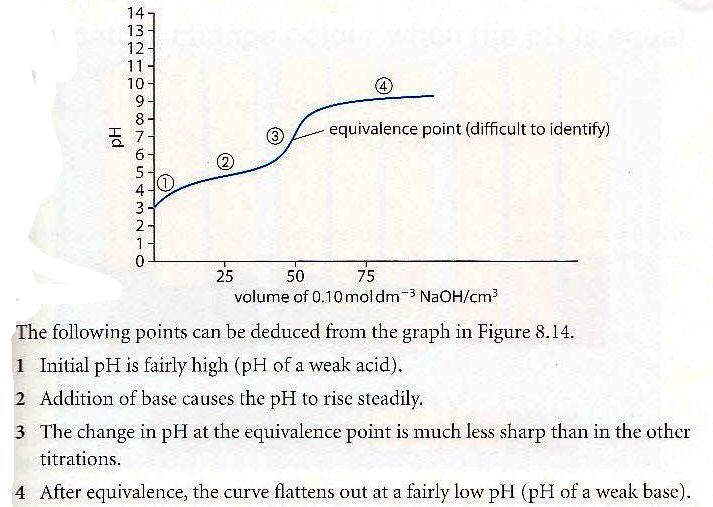

At the point halfway to equivalence pH=pKa or pOH=pKb and pH+pOH = 14. This allows you to find pKa or pKb from the curve.
An indicator is a substance that change color according to the pH of the solution.
Indicators work by setting up a weak acid/base equilibrium where the acid and its conjugate base have different colors.
HIn(aq) <=> H+(aq) + In-(aq).
Where HIn is one colour and In is the other.
The endpoint of an indicator is the pH where it changes color.
At this point pH=pKa.
The idea is to choose and indicator that has its endpoint in the same pH-range where the titration curve has its equivalence point (the point where equal amounts of the base and acid in the titration neutralize each other). In this way the indicator signals when equivalence is reached.