
0 - What does Δ (delta) in for example Δx mean ?
1 - What is the difference between distance and displacements ?
2 - What is the difference between speed and velocity ?
4 - What is the average speed and velocity ?
5 - What is the instantaneous speed and velocity ?
7 - What is uniform motion and acceleration ?
8 - What is the SUVAT formulas for uniform acceleration ?
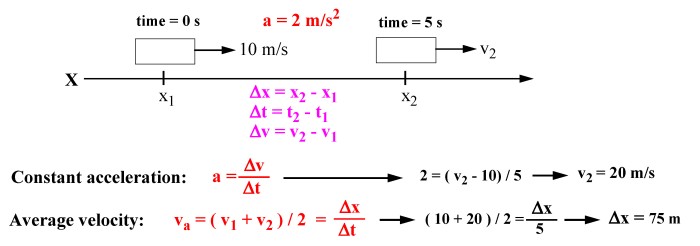
9 - A car travelling at 10 m/s accelerates at 2 m/s2 for 5s. What is its displacement ?
10 - A car is travelling at 10 m/s with uniform motion. What is its displacement after 5s ?
13 - How do you get velocity in a displacement-time graph and acceleration in a velocity-time graph ?
14 - How do you calculate the displacement in a velocity-time graph ?
15 - What can you calculate from the area in an acceleration-time graph ?
16 - What is the velocity and acceleration if you drop something in vacuum ?
17 - What is the velocity and acceleration if you drop something in air ?
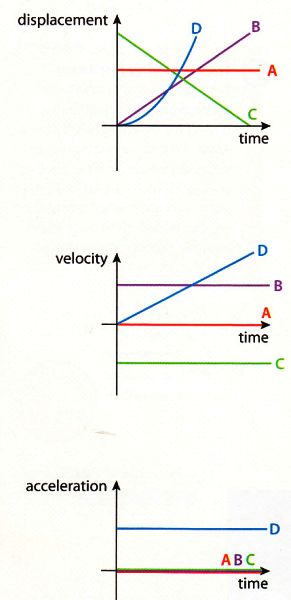
19 - What sort of motion do the lines called A describe ?
20 - What sort of motion do the lines called B describe ?
21 - What sort of motion do the lines called C describe ?
22 - What sort of motion do the lines called D describe ?
23 - What does it means that the forces are balanced ?
24 - Draw a picture of a block on a slope with balanced forces.
25 - What are the equations for a block on a slope with balanced forces ?
26 - How do you calculate the force W (the weight) ?
27 - What is Newton's first law of motion ?
29 - Use Newton's first law to explain what happens to a car moving with a constant velocity.
30 - Use Newton's first law to explain what happens to a car if the engine is turned off.
31 - What condition is needed to have translational equilibrium ?
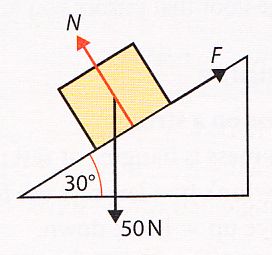
32 - The block above is in translational equilibrium. Calculate the forces.
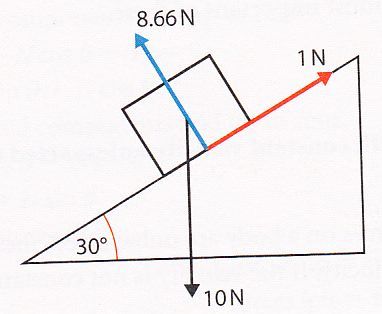
33 - The block above is not in translational equilibrium. Calculate the resulting force on the block.
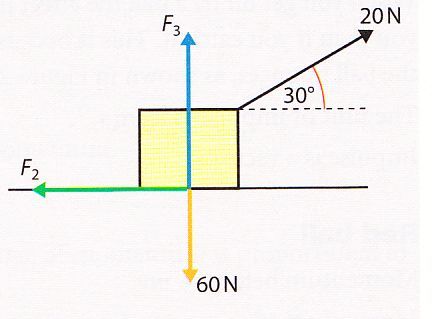
34 - The block above is in translational equilibrium. Calculate the forces.
35 - What is momentum ?
36 - What is impulse ?
37 - What is Newton's second law of motion ?
38 - A 500 kg heavy elevator is accelerating upwards with 1 m/s2. What is the tension in the cables ?
39 - A 500 kg heavy elevator is accelerating downwards with 1 m/s2. What is the tension in the cables ?
40 - Which of the following quantities are scalars and which are vectors: m, p, I, v, a, F, t ?
41 - What is Newton's third law ?
42 - Apply Newton's third law on a box sitting on the floor !
43 - Apply Newton's third law on an object falling in the earths gravitational field !
44 - What does the law of conservation of momentum say ?
45 - The law of momentum conservation only works if the system is isolated, what does that mean ?
46 - Can you apply the law of momentum conservation to a ball hitting a wall ?
47 -
Can you apply the law of momentum conservation to a ball hitting the wall of a spaceship ?

48 - Assume that the picture above shows an isolated system. Calculate v.
49 - What is work ?
54 - How can you calculate the work if the force is not constant ?
55 - What is energy ?
56 - Name a few different forms of energy !
57 - There is a law about energies. What does it say ?
59 - What is potential energy ?
62 - What is an elastic collision ?
63
Calculate v1 and v2 in the following elastic collision: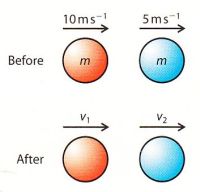
64 - What is power ?
66 - What is efficiency ?
68 - What is the time period for circular motion ?
69 - What is the frequency for circular motion ?
70 - What is angular velocity ?
71 -
What are the formulas for the centripetal force ?
Δx = xfinal - xinitial so Δ mean that one take the difference between two values.
Only high level stuff
Look at the data booklet: Energy is the capacity of a system to do work on other systems. Unit: Joule (J) Some of the many forms that energy takes are: - Potential energy, stored in a system. - Kinetic energy, from the movement of matter. The law of conservation of energy:
The time period (T) in circular motion is the time it takes for one complete turn. Unit: s
Displacement is a vector. Unit = m.
Distance is a scalar (a number), it is the length that has been travelled. Unit = m.
Velocity is a vector. It is defined as Velocity = displacement / time . Unit = m/s .
Speed is a scalar (a number). It is defined as Speed = distance / time . Unit = m/s .
Acceleration is a vector. It is defined as Acceleration = change of velocity / time . Unit = m/s2 .
Formula: a = (v - u) / Δt
where v is the velocity at time t1 and u the velocity at time t2 and Δt = t2 - t1
Average speed and velocity is when one averages over a long time (t). During this time the velocity and
speed might go up and down.
The formula to use for the calculation is v = s / t
where s is displacement if the velocity is calculated and s is distance if the speed is calculated.
Instantaneous speed and velocity is the speed and velocity at a specific moment in time. It has to be calculated
with
v = δx / δt
, where v is the velocity or speed during a short time interval (δt) when the distance travelled in that time interval is δx.
It is 20km from Lund to Malmö and a car drives from Malmö to Lund and then back to Malmö in 0.4 hours.
The distance is then 40 km. The displacement is then 0 km. The speed is 40/0.4=100 km/h. The velocity is 0/0.4=0 .
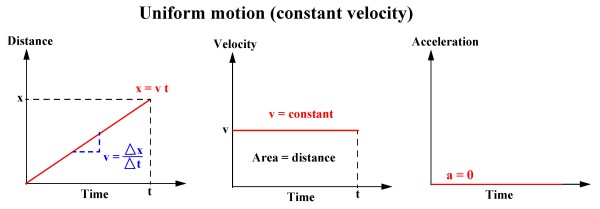
Uniform motion (or velocity) is motion when the velocity is constant (it does not change).
Uniform acceleration is motion when the velocity is not constant but the acceleration is constant.
So the change of the velocity (=acceleration) is constant.
First look at the data booklet:
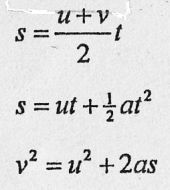


Uniform motion means that the velocity is constant and the acceleration is therefore zero. A graph of displacement
versus time shows a straight line with its gradient being the velocity. A graph of velocity versus time is therefore a constant line
and a graph of acceleration versus time is empty since the acceleration is zero.
Uniform acceleration means that the velocity is not constant but that the acceleration is constant.
A graph of displacement versus time shows a parabola. A graph of velocity versus time is a straight line with
its gradient being the acceleration. A graph of acceleration versus time is a constant line.
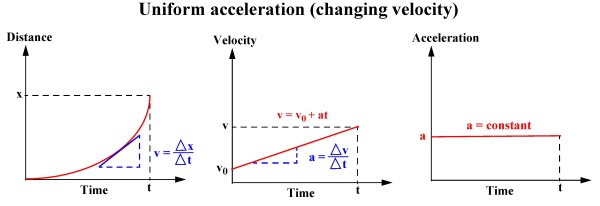
Draw the tangent to the curve at the time you want to get velocity or acceleration and calculate the gradient (slope)
of the tangent. That is equal to calculating v = δS / δt and a = δv / δt .
The displacement can be calculated in a velocity-time graph because it is equal to the area under the graph.
The area under the curve in an acceleration-time graph give the change in velocity Δv = v - u.
2.2 - Free fall motion
The acceleration on the earth and in vacuum is a = g = 9.82 m/s. This means that the velocity if one drops something
in vacuum is always increasing.
The acceleration on the earth and in air is a = g = 9.82 m/s. However, the air will cause a force from air resistance
that will slow down the acceleration until it is eventually zero (if it can fall long enough).
The velocity is then constant and will not increase anymore.
2.3 - Graphical representation of motion
2.4 - Projectile motion
2.5 - Forces and dynamics
2.6 - Newton's laws of motion
A moving car that has the engine turned off will no longer have its forces balanced.
There will be no force created by the engine that turns the wheels and creates a
friction force between the tires and the road. But the force from air resistance will
still be there. So the velocity will slow down (there will be a de-acceleration) due
to the air resistance force. The Newton's first law is NOT applicable since the forces
are not balanced. However, after some time the car will be standing still and no air resistance
force is then working on the car and now Newton's first law is applicable.
In order to have translational equilibrium all the forces on a body have to be balanced.
2.7 - The relationship between force and acceleration
2.8 - Newton's third law
An isolated system is a system on which no external forces are working.2.9 - Work, energy and power

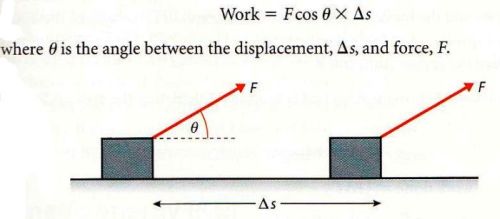
Work: W = F•Δs = Force x Distance moved in the direction of the force
i) Energy cannot be created or destroyed - it is constant.
ii) It can only be changed from one form to another.
An elastic collision is a collision where the momentum and energy is conserved.
ε = Wout / Win → Efficiency = useful work out / energy put in Unit: %
2.10 - Uniform circular motion