Standard signals
Traffic
lights
Signal
boards
Signals may appear on different boards like:
![]()
![]()
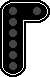
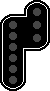
However, the position of lights is always the same, so:
![]() is the same signal as
is the same signal as 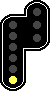
Flashing
lights
![]() designates a flashing light
designates a flashing light
![]() designates a fixed light
designates a fixed light
Track
monitor colors
The signaling of the route is now very close to the real one and has been
carefully designed so that you don't have to use the track monitor to drive
safely (the track monitor doesn't exist in the real world and drivers can only
rely on signals). Of course, you can still use the track monitor, but it won't
tell you everything. Instead of directly displaying the color of signals, it
will only give you some clues about them:
|
TM color |
Meaning |
Possible signals (see individual
descriptions) |
|
Green |
Clear or
not very restrictive signal |
Clear Pre-warning Slow down warning (30 or 60) 60 km/h slow down (not combined with a warning) |
|
Yellow |
Warning or equivalent |
Warning 60 km/h slow down + warning 30 km/h slow down |
|
Red |
Stop or restrictive signal |
Stop, semaphore, shunting signal |
Signal
aspects
|
|
Clear |
|
|
This
signal means |
At least
the next 3 blocks are clear. |
|
|
What to
do |
You can
run at full speed. |
|
|
Track
monitor color |
GREEN |
|
|
Track
monitor text |
CLEAR |
|
|
Pre warning |
|
|
This
signal means |
Next
signal is a warning. |
|
|
What to
do |
Watch your
speed: you may have to stop your train after the next signal. |
|
|
Track
monitor color |
GREEN |
|
|
Track
monitor text |
CLEAR |
|
|
Warning |
|
|
This
signal means |
Be ready to
stop before the next signal. This is a very important signal and a warning
should never be treated "lightly". Most
people assume that the next signal after a warning is a semaphore or a stop,
but there are many other situations where a warning can appear, for example
before a shunting or repeated slow down signal (see below). Just remember one
thing: when you see this signal, be ready to stop. |
|
|
What to
do |
Slow down
in order to stop before the next signal. |
|
|
Track
monitor color |
YELLOW |
|
|
Track monitor
text |
APPROACH |
|
|
Semaphore |
|
|
This
signal means |
There is
a train in the next block. |
|
|
What to
do |
Stop in
front of this signal. This signal is passable, so you have the option to
proceed at 30 km/h or wait for a clear signal. Note that
if you proceed and the train in the next block is stopped, you will
eventually reach it, so be prepared to stop at any time. Also,
note that passing a semaphore requires you to drive at 30 km/h through the
whole block, so it's not always the best choice. Depending on the situation,
you may prefer to wait for a clear indication before entering the block. |
|
|
Track
monitor color |
RED |
|
|
Track
monitor text |
STOP AND
PROCEED |
|
|
Stop (also known as "red square") |
|
|
This
signal means |
For
security reasons, the next block cannot be entered. This signal is typically
used to protect switches. |
|
|
What to
do |
Stop in
front of the signal and wait for a clear indication. Trying to pass this
signal will immediately end any activity. |
|
|
Track
monitor color |
RED |
|
|
Track
monitor text |
STOP |
|
|
60 km/h slow down warning |
|
|
This
signal means |
Next
signal is a 60 km/h slow down. |
|
|
What to
do |
Reduce
your speed in order to pass the next signal at 60 km/h. This signal
can be combined with a pre-warning, but will be cancelled by a warning, a
semaphore or a stop. When
combined with a pre-warning, just apply both signals' recommendations. |
|
|
Track
monitor color |
GREEN |
|
|
Track
monitor text |
CLEAR |
|
|
60 km/h slow down |
|
|
This
signal means |
You are
reaching a switch that requires a 60 km/h slow down. |
|
|
What to
do |
You must
pass this signal at 60 km/h (the switch that requires the slow down may be
identified by a "V" sign on the ground). This signal
can be combined with a pre-warning or a warning, but will be cancelled by a
semaphore or a stop. When
combined with a pre-warning or warning, just apply both signals'
recommendations. |
|
|
Track
monitor color |
GREEN if SD60 or SD60 + pre-warning YELLOW if SD60 + warning |
|
|
Track
monitor text |
CLEAR if SD60 or SD60 + pre-warning APPROACH if SD60 + warning |
|
|
30 km/h slow down warning |
|
|
This
signal means |
Next
signal is a 30 km/h slow down. |
|
|
What to
do |
Reduce your
speed in order to pass the next signal at 30 km/h. This
signal will be cancelled by a warning, a semaphore or a stop, but will cancel
a pre-warning. |
|
|
Track
monitor color |
GREEN |
|
|
Track
monitor text |
CLEAR |
|
|
30 km/h slow down |
|
|
This
signal means |
You are
reaching a switch that requires a 30 km/h slow down. |
|
|
What to
do |
You must
pass this signal at 30 km/h (the switch that requires the slow down may be
identified by a "V" sign on the ground). This
signal can be combined with a pre-warning or a warning, but will be cancelled
by a semaphore or a stop. When
combined with a pre-warning or warning, just apply both signals'
recommendations. |
|
|
Track
monitor color |
YELLOW |
|
|
Track
monitor text |
APPROACH |
|
|
Shunting track free |
|
|
This
signal means |
You are
in a shunting area and the track is clear. |
|
|
What to
do |
Never
assume anything about the state of the next signal, as you are in a shunting
area: you can proceed at 30 km/h max and must be ready to stop at any time. |
|
|
Track
monitor color |
RED |
|
|
Track
monitor text |
RESTRICTING |
|
|
Shunting stop (also known as "violet
square") |
|
|
This
signal means |
The next
block cannot be entered for security reasons. This signal is typically used
to protect trains in shunting areas. |
|
|
What to
do |
Stop in
front of the signal and wait for a clear indication. Trying to pass this
signal will immediately end any activity. |
|
|
Track
monitor color |
RED |
|
|
Track
monitor text |
STOP |
|
|
Distant direction indicator |
|
|
This
signal means |
1 white
light: you will go to the left after the next switch. 2 white
lights: you will go to the right after the next switch. Please
note this is a "geographic" direction: if one of the tracks goes
left at the switch, then pass over or under the other and goes to the right,
you will get a "right" indication. |
|
|
What to
do |
This
signal is informational only. |
|
|
Track
monitor color |
- |
|
|
Track
monitor text |
- |
Signal
combinations
Q: What
does this signal mean?
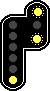
A: It's a
60 km/h slow down (upper flashing yellow lights) + warning (lower yellow
light).
Meaning:
you must slow down at 60 km/h (definition of SD60) and be ready to stop before
the next signal (definition of a warning).
Q: What
signal will announce the SD60+Warning?
A: The 60
km/h slow down must be announced by a 60 km/h slow down warning, and the warning
must be announced by a pre-warning:
 60
km/h slow down warning (upper flashing lights) + pre-warning (lower flashing
light)
60
km/h slow down warning (upper flashing lights) + pre-warning (lower flashing
light)
Meaning:
next signal is a 60 km/h slow down (definition of SD60 warning) and next signal
is a warning (definition of pre-warning). So, next signal is a SD60+warning.
Slow
down series
If a switch
that must be passed at 60 km/h is followed by another that must be passed at 30
km/h, the signal before the first switch should be both a SD60 (2 vertical
flashing yellow lights) and a SD30 warning (2 horizontal yellow lights).
Actually,
for visibility reasons, the second indication is replaced by a warning, so the
double "SD60/SD30 warning" signal is replaced by:
 SD60 +
warning
SD60 +
warning
The same
technique is used for other slow down series and there are never more than 3
lights on a signal board.
F
and Nf signals
The letter
F, "Franchissable" in French, means "passable".
Signals
having a F plate can always be passed, even in their most restrictive state,
which is a semaphore (one red light). F signals are used to space trains on the
same track, going in the same direction. As they are passable, they provide the
best possible train flow.
On the
other hand, signals having a Nf plate cannot be passed in their most
restrictive state, which is a stop, also known as "red square" (two red lights). They are typically used
to protect switches and avoid lateral or frontal collisions.
The
white light
You will
notice Nf signals have an additional little white light on the left. It is lit
only when the signal is passable, so you will see it on warnings, slow downs,
etc… but never on stops (red or violet squares).
You may ask
what's the purpose of this light, as we already know only stops can't be
passed?
Here is the
explanation:
If a lamp
on a red square is burned out, you may think it's a semaphore and pass it,
which may be very dangerous. This little white light will save your life! Here
is how:
When you
see a signal with only one red light:
1. Look at the plate, if it's F, it's a
semaphore and you can pass it safely.
2. If the plate is Nf and you see the
white light, it's a semaphore again, so you can pass it.
3. If the plate is Nf and you don't see
the white light, then it's a red square, but one of the red lights is burned
out, so you will stop and wait for a
clear indication.
…And what
if the white light itself is burned out?
By
definition, Nf signals with no white light are not passable, so you will not
pass it. When the signal becomes yellow or green, you will notice there is still
no white light, so you will simply have to write down the identification number
of the signal and ask the maintenance team to change the burned out white
light.
Speed
limitations
They can
appear with or without a warning:
Without warning (when the upcoming speed limitation is greater than the current one)
![]() 80 km/h speed limitation
80 km/h speed limitation
With a warning (when the upcoming speed limitation is lower than the current one)
 Warning used when the speed difference is
greater than 40 km/h
Warning used when the speed difference is
greater than 40 km/h
![]() Warning used when the speed difference
is lower than 40 km/h
Warning used when the speed difference
is lower than 40 km/h
![]() Start of speed limited zone
Start of speed limited zone
![]() End of speed limited zone (max route
speed allowed)
End of speed limited zone (max route
speed allowed)
Other
signals
![]() Use the horn
Use the horn
 Buffer at 150 m
Buffer at 150 m
![]() Switch location (used for "important"
switches, like the beginning of a new route)
Switch location (used for "important"
switches, like the beginning of a new route)
Approach
signs: they are used to warn the driver, when the upcoming signal is hard to
see (for example, when it's in a curve)
|
-300 m |
-200 m |
-100 m |
0 |
|
|
|
|
Signal with bad visibility |
Last modified 06/18/2004